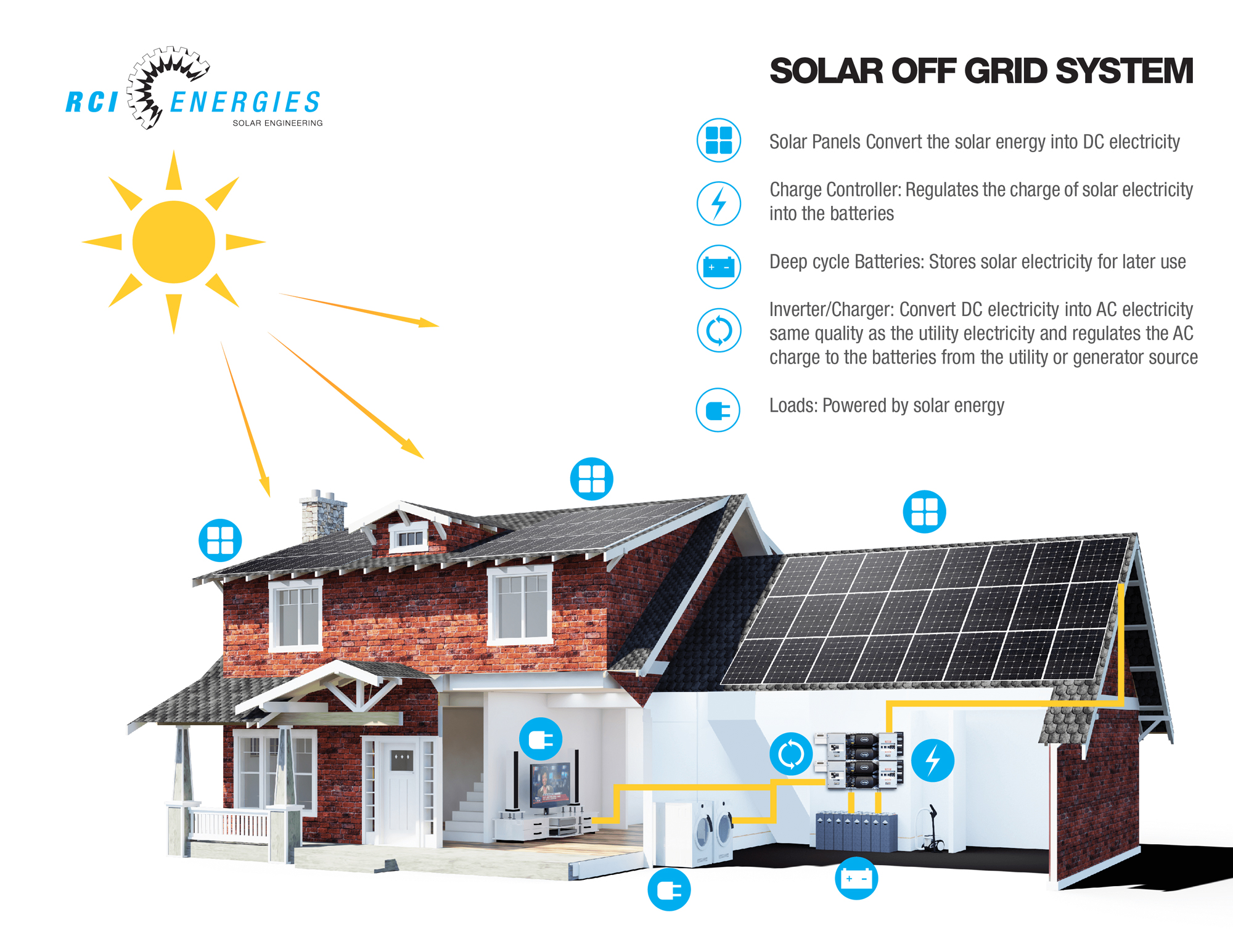
Unveiling the intricacies of off grid solar prices, this guide embarks on an illuminating journey, exploring the factors that shape the cost of harnessing the sun’s energy for independent living.
Delving into the heart of off grid solar systems, we unravel the interplay of panel efficiency, battery capacity, and inverter selection, deciphering their impact on overall expenses.
Cost Components of Off-Grid Solar Systems
Understanding the cost components of an off-grid solar system is essential for making informed decisions about your investment. This system’s overall expense is influenced by several factors, including the efficiency of solar panels, the capacity of batteries, and the type of inverter used.
Here’s a breakdown of the typical costs associated with each component:
Solar Panels
The cost of solar panels depends on their efficiency, measured in percentage. Higher efficiency panels produce more electricity per square foot, reducing the number of panels needed and lowering overall system costs. However, they are typically more expensive than lower-efficiency panels.
Batteries
Battery capacity is measured in amp-hours (Ah) and determines how much electricity the system can store. Larger battery capacities allow for longer periods of autonomy but come with a higher price tag. The type of battery (e.g., lead-acid, lithium-ion) also affects the cost.
Inverters
Inverters convert the DC electricity produced by solar panels into AC electricity used by appliances. The cost of an inverter depends on its power output, measured in watts. Higher-wattage inverters can handle more electrical loads but are more expensive.
Other Costs, Off grid solar prices
In addition to the main components, other costs to consider include:
- Mounting hardware for solar panels
- Wiring and electrical materials
- Installation labor
- Maintenance and repairs
System Size and Location
The size of the solar system (measured in kilowatts) and its location can also impact overall expenses. Larger systems require more components and installation time, increasing the total cost. Remote locations may have higher transportation and labor costs.
Comparing Different Off-Grid Solar System Designs: Off Grid Solar Prices
Off-grid solar systems offer a reliable and sustainable energy solution for remote areas or locations with unreliable grid connections. Understanding the key differences between various off-grid solar system designs is crucial for choosing the most suitable system for your specific needs.
Grid-Tied Solar Systems
Grid-tied solar systems are connected to the utility grid, allowing excess solar energy generated to be exported and sold back to the grid. This design is suitable for homeowners who want to reduce their electricity bills and contribute to the grid’s energy supply.
Advantages:
- Lower upfront costs compared to other off-grid systems.
- Reduced energy consumption from the grid, leading to savings on electricity bills.
- No need for battery storage, as excess energy can be exported to the grid.
Disadvantages:
- Dependence on the utility grid for backup power during outages.
- May require grid interconnection approval and compliance with local regulations.
Hybrid Solar Systems
Hybrid solar systems combine grid connection with battery storage, providing both grid independence and backup power during outages. This design is ideal for areas with frequent grid outages or those seeking a higher level of energy independence.
Advantages:
- Reduced reliance on the grid, providing backup power during outages.
- Can store excess solar energy for later use, reducing grid dependence.
- Eligible for tax incentives and rebates in some areas.
Disadvantages:
- Higher upfront costs due to the addition of battery storage.
- Battery maintenance and replacement costs over time.
Stand-Alone Solar Systems
Stand-alone solar systems are completely independent of the grid, relying solely on solar energy and battery storage. This design is suitable for remote locations or areas with no grid access.
Advantages:
- Complete energy independence, eliminating reliance on the grid.
- No grid interconnection or approval required.
- Can be customized to meet specific energy needs and usage patterns.
Disadvantages:
- Highest upfront costs among off-grid systems due to extensive battery storage.
- Careful system sizing and design is essential to ensure adequate power supply throughout the year.
Estimating Energy Needs for Off-Grid Living
Estimating energy consumption is a critical step in designing an off-grid solar system to ensure it meets your energy needs. Various factors influence energy consumption, including household size, appliance usage, and climate. An energy audit can help you calculate your daily, weekly, and monthly energy requirements.
Energy Audit
An energy audit involves assessing your current energy consumption to identify areas where you can improve efficiency and reduce usage. You can conduct an energy audit by:
- Tracking your energy usage with a smart meter or energy monitoring device.
- Analyzing your utility bills to identify peak usage times and high-consumption appliances.
- Conducting a home energy assessment to identify areas of energy loss and potential improvements.
Based on the energy audit results, you can estimate your daily, weekly, and monthly energy needs. This information is essential for determining the size and capacity of your off-grid solar system.
Further details about garden solar panel kits is accessible to provide you additional insights.
DIY vs. Professional Installation of Off-Grid Solar Systems
Deciding whether to install an off-grid solar system yourself or hire a professional is a crucial decision that can impact the system’s performance, safety, and longevity. Both approaches have their advantages and drawbacks, which should be carefully considered before making a choice.
Get the entire information you require about sustainable tourism destinations examples on this page.
DIY Installation
DIY installation can be a cost-effective option for those with electrical wiring and solar panel mounting experience. It allows for greater flexibility and control over the system design and installation process. However, it also requires a significant amount of technical knowledge and skills, including:
- Electrical wiring: Understanding electrical circuits, wire sizing, and proper connections.
- Panel mounting: Selecting appropriate mounting hardware and ensuring panels are securely and safely installed.
- Battery management: Selecting and maintaining batteries, including proper charging and discharging practices.
Pros:
For descriptions on additional topics like cheap home solar power kits, please visit the available cheap home solar power kits.
- Cost savings: Can be significantly cheaper than professional installation.
- Flexibility: Allows for customization and tailoring the system to specific needs.
- Educational value: Provides an opportunity to learn about solar system design and installation.
Cons:
- Safety risks: Electrical work can be hazardous and requires proper precautions.
- Efficiency concerns: Improper installation can lead to reduced system efficiency and potential damage.
- Warranty coverage: DIY installations may void manufacturer warranties, limiting protection against defects.
Professional Installation
Hiring a qualified professional installer offers several advantages, including:
- Expertise and experience: Certified installers have the knowledge and experience to design and install systems safely and efficiently.
- Safety assurance: Professionals follow industry standards and codes, ensuring proper electrical connections and minimizing safety hazards.
- Warranty coverage: Professional installations typically come with warranties that cover both materials and workmanship, providing peace of mind.
Pros:
- Quality assurance: Ensures a professionally designed and installed system that meets performance expectations.
- Safety compliance: Adherence to electrical codes and standards minimizes safety risks.
- Warranty protection: Provides coverage against defects and ensures system longevity.
Cons:
- Cost: Professional installation can be more expensive than DIY.
- Limited flexibility: Installers may have standard designs or package options that may not fully align with specific needs.
- Scheduling constraints: Availability of qualified installers can impact project timelines.
Ultimately, the decision between DIY and professional installation depends on individual circumstances, skills, and budget. Those with the necessary electrical knowledge and experience may consider DIY to save costs and gain hands-on experience. However, those prioritizing safety, efficiency, and warranty coverage should consider hiring a qualified professional installer.
Government Incentives and Financing Options for Off-Grid Solar
Government incentives and financing options can significantly reduce the upfront cost of installing an off-grid solar system. These incentives vary depending on location and may include tax credits, rebates, and low-interest loans. Understanding these incentives and navigating the application process can help you maximize your savings on your off-grid solar system.
Eligibility Criteria and Application Process
Eligibility for government incentives typically depends on factors such as the type of solar system installed, the location of the property, and the applicant’s income level. The application process usually involves submitting a completed application form along with supporting documentation, such as proof of purchase and installation.
Remember to click ecotourism uk to understand more comprehensive aspects of the ecotourism uk topic.
It’s important to carefully review the eligibility criteria and application requirements to ensure a successful application.
Impact on Overall Cost
Government incentives can substantially reduce the overall cost of an off-grid solar system. Tax credits, for example, allow you to deduct a certain percentage of the cost of your solar system from your federal income taxes. Rebates provide a direct cash payment that can be used to offset the upfront cost of installation.
Low-interest loans can make it more affordable to finance the installation of your solar system over time.
Strategies for Maximizing Savings
To maximize savings on your off-grid solar system, consider the following strategies:
- Research available incentives in your area.
- Apply for all eligible incentives.
- Install a solar system that meets the eligibility criteria for incentives.
- Consider financing options that offer low interest rates.
- Take advantage of any available rebates or discounts.
Conclusion
As we conclude our exploration of off grid solar prices, a tapestry of insights emerges, empowering you to make informed decisions about embracing sustainable energy solutions. Whether embarking on a DIY installation or seeking professional assistance, this guide serves as an invaluable compass, navigating the path towards energy independence.
User Queries
What factors influence the cost of an off grid solar system?
The cost of an off grid solar system is influenced by factors such as panel efficiency, battery capacity, inverter type, system size, and location.
What are the advantages of a grid-tied solar system?
Grid-tied solar systems allow excess energy to be sold back to the grid, potentially generating additional income.
How can I estimate my energy needs for off-grid living?
Conduct an energy audit to determine your daily, weekly, and monthly energy consumption patterns, considering factors such as household size, appliance usage, and climate.